Cloud Based Encryption: Protecting Your Data in the Digital Age
Introduction
In the age of digital advancement, ensuring the security of our sensitive data has become a matter of utmost importance. With the rising number of cyber threats and data breaches, it is crucial to establish robust encryption measures to protect our information. One increasingly popular solution for achieving this is cloud-based encryption. In this article, we will delve into the concept of cloud-based encryption, its advantages, and its role in safeguarding your data. So, let us embark on a journey to explore the realm of cloud-based encryption!
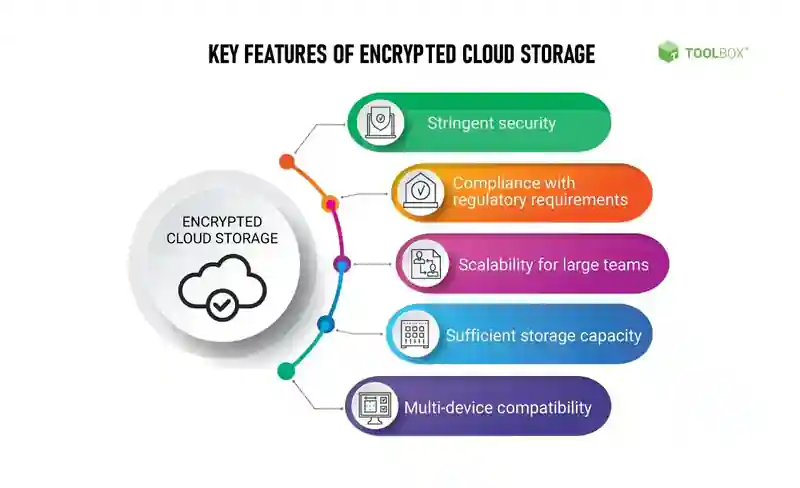
Table of Contents
- What is Cloud Based Encryption?
- How Does Cloud Based Encryption Work?
- Benefits of Cloud Based Encryption
- The Role of Key Management in Cloud Based Encryption
- Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Based Encryption
- Cloud Based Encryption vs. Traditional Encryption Methods
- Addressing Concerns about Cloud Based Encryption
- The Future of Cloud Based Encryption
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How secure is cloud-based encryption?
- Can cloud-based encryption be used for all types of data?
- Does cloud-based encryption impact performance?
- How do I choose the right cloud-based encryption solution for my organization?
- What are the potential drawbacks of cloud-based encryption?
- Is cloud-based encryption compliant with data privacy regulations?
- Conclusion
1. What is Cloud Based Encryption?
Cloud-based encryption refers to the process of encrypting data before it is stored or transmitted to a cloud service provider. It involves converting plaintext data into ciphertext, making it unreadable to unauthorized individuals. This encryption process ensures that even if the data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties, it remains secure and unintelligible.
2. How Does Cloud Based Encryption Work?
Cloud-based encryption operates on the principle of using encryption algorithms to transform data into an unreadable format. When data is uploaded to the cloud, it is encrypted locally on the client-side before transmission. The encrypted data is then securely transmitted and stored in the cloud. When the data needs to be accessed, it is decrypted using encryption keys, which are managed by the cloud service provider or the data owner.
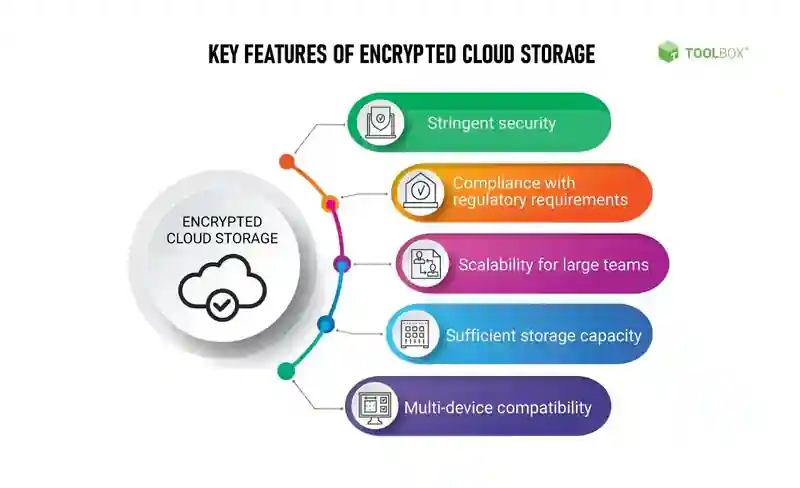
3. Benefits of Cloud Based Encryption
Implementing cloud-based encryption offers several benefits for organizations and individuals looking to secure their data. Some of the key advantages include:
-
Enhanced Data Security: Cloud-based encryption ensures that data remains secure, even if it falls into the wrong hands. By encrypting data before transmission or storage, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
-
Improved Compliance: Many industries have strict data privacy regulations and compliance requirements. Cloud-based encryption helps organizations meet these regulations by providing an extra layer of security to sensitive data.
-
Data Sovereignty: Cloud-based encryption allows organizations to retain control over their data. With the encryption keys in their possession, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure and protected, even when stored on third-party cloud servers.
-
Seamless Collaboration: Cloud-based encryption enables secure collaboration and sharing of sensitive information. Authorized users can access and decrypt encrypted data, facilitating seamless collaboration while maintaining data security.
-
Cost Savings: By leveraging cloud-based encryption services, organizations can avoid the upfront costs associated with building and maintaining their own encryption infrastructure. This makes encryption more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
4. The Role of Key Management in Cloud Based Encryption
Effective key management is crucial for the success of any encryption system, including cloud-based encryption. Encryption keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data, and their protection is essential to maintain the security of encrypted information.
In cloud-based encryption, the responsibility for key management can vary depending on the implementation. Some organizations prefer to manage their encryption keys on-premises, while others opt for a key management service provided by the cloud service provider. Regardless of the approach, proper key management practices, such as secure key storage, rotation, and access controls, are necessary to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data.
5. Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Based Encryption
When implementing cloud-based encryption, it is essential to follow best practices to maximize its effectiveness. Some key considerations include:
-
Data Classification: Conduct a thorough assessment of your data and classify it based on its sensitivity. Not all data may require the same level of encryption, and this classification will help determine the appropriate encryption measures for each data category.
-
Encryption Strength: Choose encryption algorithms and key lengths that align with industry best practices. Strong encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), coupled with appropriate key lengths, enhance the security of encrypted data.
-
Secure Key Management: Implement robust key management practices to protect encryption keys from unauthorized access. This includes secure key storage, regular key rotation, and strict access controls.
-
Multi-Layered Security: Combine cloud-based encryption with other security measures, such as strong authentication mechanisms and network security controls, to create a multi-layered security approach.
6. Cloud Based Encryption vs. Traditional Encryption Methods
Cloud-based encryption differs from traditional encryption methods in several ways. While traditional encryption typically involves encrypting data on local devices or servers, cloud-based encryption extends the encryption process to the cloud environment. This enables organizations to secure data throughout its lifecycle, from transmission to storage.
Additionally, traditional encryption methods may require organizations to invest in dedicated encryption hardware or software, whereas cloud-based encryption leverages the infrastructure and services provided by the cloud service provider. This can result in cost savings and simplified management for organizations.
7. Addressing Concerns about Cloud Based Encryption
As with any technology, cloud-based encryption comes with its fair share of concerns. However, it is important to address these concerns to make informed decisions about its implementation. Some common concerns and their corresponding explanations include:
-
Data Privacy: Cloud-based encryption enhances data privacy by ensuring that sensitive information remains encrypted and inaccessible to unauthorized parties. By leveraging strong encryption algorithms and proper key management practices, organizations can maintain control over their data and mitigate privacy risks.
-
Performance Impact: While encryption does add some overhead, modern encryption algorithms are designed to minimize performance impact. Additionally, advancements in cloud computing infrastructure have significantly reduced the performance impact of cloud-based encryption, making it a viable option for most organizations.
-
Data Loss: Cloud service providers typically implement robust backup and redundancy measures to protect against data loss. By choosing a reputable and reliable cloud service provider, organizations can mitigate the risks of data loss and ensure the availability of their encrypted data.
8. The Future of Cloud Based Encryption
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, cloud-based encryption will play a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of data. With advancements in encryption algorithms, key management practices, and cloud computing infrastructure, we can expect even more robust and efficient cloud-based encryption solutions in the future. As organizations become increasingly reliant on cloud services, the demand for secure encryption measures will only continue to grow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How secure is cloud-based encryption?
Cloud-based encryption provides a high level of security for sensitive data. By using strong encryption algorithms and implementing proper key management practices, organizations can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their data, even when stored or transmitted through the cloud.
2. Can cloud-based encryption be used for all types of data?
Yes, cloud-based encryption can be used for various types of data, including text documents, databases, multimedia files, and more. The encryption process is agnostic to the type of data and focuses on securing the underlying information.
3. Does cloud-based encryption impact performance?
While encryption does add some performance overhead, modern encryption algorithms are designed to minimize this impact. Additionally, advancements in cloud computing infrastructure have significantly reduced the performance impact of cloud-based encryption, making it a viable option for most organizations.
4. How do I choose the right cloud-based encryption solution for my organization?
When choosing a cloud-based encryption solution, consider factors such as the encryption algorithms used, key management capabilities, integration with existing systems, compliance with data privacy regulations, and the reputation and reliability of the cloud service provider. Conduct thorough evaluations and assessments to ensure the selected solution meets your organization's specific requirements.
5. What are the potential drawbacks of cloud-based encryption?
Some potential drawbacks of cloud-based encryption include reliance on third-party cloud service providers, potential concerns over data privacy, and the need for proper key management practices. Organizations must carefully evaluate these factors and address any concerns to ensure a successful implementation.
6. Is cloud-based encryption compliant with data privacy regulations?
Cloud-based encryption can help organizations meet data privacy regulations by providing an additional layer of security to sensitive data. However, compliance with specific regulations depends on various factors, including the encryption algorithms used, key management practices, and the overall security posture of the organization. It is essential to understand the regulatory requirements applicable to your industry and work with legal and compliance teams to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
In an era where data security is paramount, cloud-based encryption offers a powerful solution to protect sensitive information. By encrypting data before transmission or storage, organizations can ensure its confidentiality and integrity, mitigating the risks of data breaches and unauthorized access. With proper key management practices and adherence to best practices, cloud-based encryption can provide a robust and scalable security solution for businesses of all sizes. Embrace the power of cloud-based encryption and safeguard your data in the digital age.